
Photo by Edho Pratama on Unsplash
You may have noticed that from the 23rd of July many websites have been branded as “not secure” in the URL bar of Google Chrome. Google’s latest update to their web browser, Chrome 68, is now flagging any websites that have not made the switch over to HTTPS. This is an effort by Google to encourage websites to take measures in securing the data of their users.
HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol. It determines how data is transferred around the web. Websites using HTTPS are encrypting the data being sent to their server. The S stands for “secure”. Google reports that 81 of the 100 top websites are now using HTTPS.
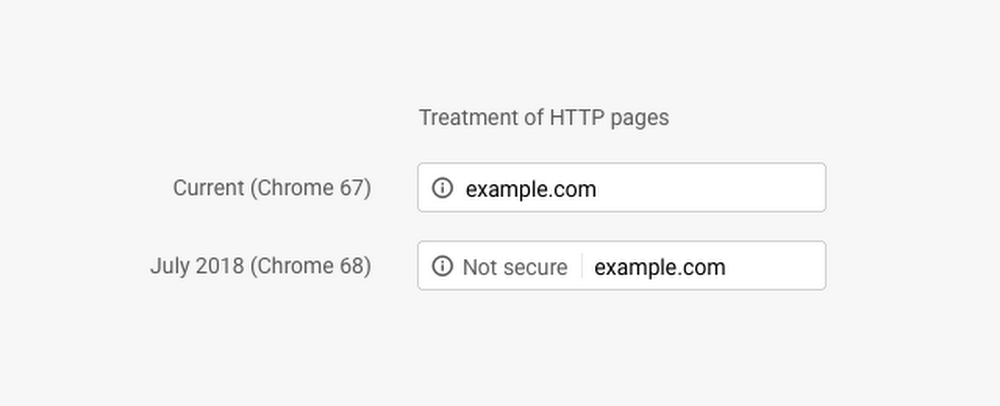
Image from blog.google
Websites without HTTPS are not encrypting the information being sent between you and the server. Hackers could potentially intercept your communications and read any information in plain text. They could potentially steal your password, bank details, and personal information like address and phone numbers. With HTTPS active however, the data is scrambled during its transference, so hackers cannot read it.
Chrome would previously flag websites as not secure if they required users to enter sensitive information such as passwords or credit card details. They have expanded this, as of the 23rd of July, to cover any website without proper encryption regardless of whether the website gathers your information.
Firefox and other large browsers are also expected to implement changes to flag insecure websites in the future.
How Does Being Flagged as Not Secure Affect a Site?
Websites that are flagged as not secure can expect a loss in business from visitors. Research suggests that over 80% of internet users would not make a transaction on a website that was flagged as not secure. HTTPS by contrast can grant a website increased trust between it and its users.
Google have also confirmed that HTTPS is a factor in their search engine rankings. Websites that are not encrypted are failing to meet their full SEO potential.
Websites that are not encrypting their data are at higher risk of being hacked or having their data stolen. This can cause tremendous lost of finances and permanent damage to their reputation.
How do I Secure my Site?
If your website is being flagged by Google Chrome as not secure, that means you need to acquire an SSL/TLS certificate. Doing this will activate HTTPS for your website. These certificates are used to prove that you own a particular domain and that your business is legitimate.
A domain validated (DV) certificate is the fastest way to get HTTPS. These certificates can be issued in minutes.
Your website will switch over to HTTPS as soon as the certificate is installed. The green padlock symbol in the URL will also indicate that your website is encrypting data.
You can find a range of SSL certificates on our website at discounted prices.




